Core Concepts
Summary: Understand the fundamental architecture, protocols, and patterns that power the SignalWire Agents SDK.
What You'll Learn
This chapter covers the foundational concepts you need to build effective voice AI agents:
- Architecture - How AgentBase and its mixins work together
- SWML - The markup language that controls call flows
- SWAIG - The gateway that lets AI call your functions
- Lifecycle - How requests flow through the system
- Security - Authentication and token-based function security
Prerequisites
Before diving into these concepts, you should have:
- Completed the Getting Started chapter
- A working agent running locally
- Basic understanding of HTTP request/response patterns
The Big Picture
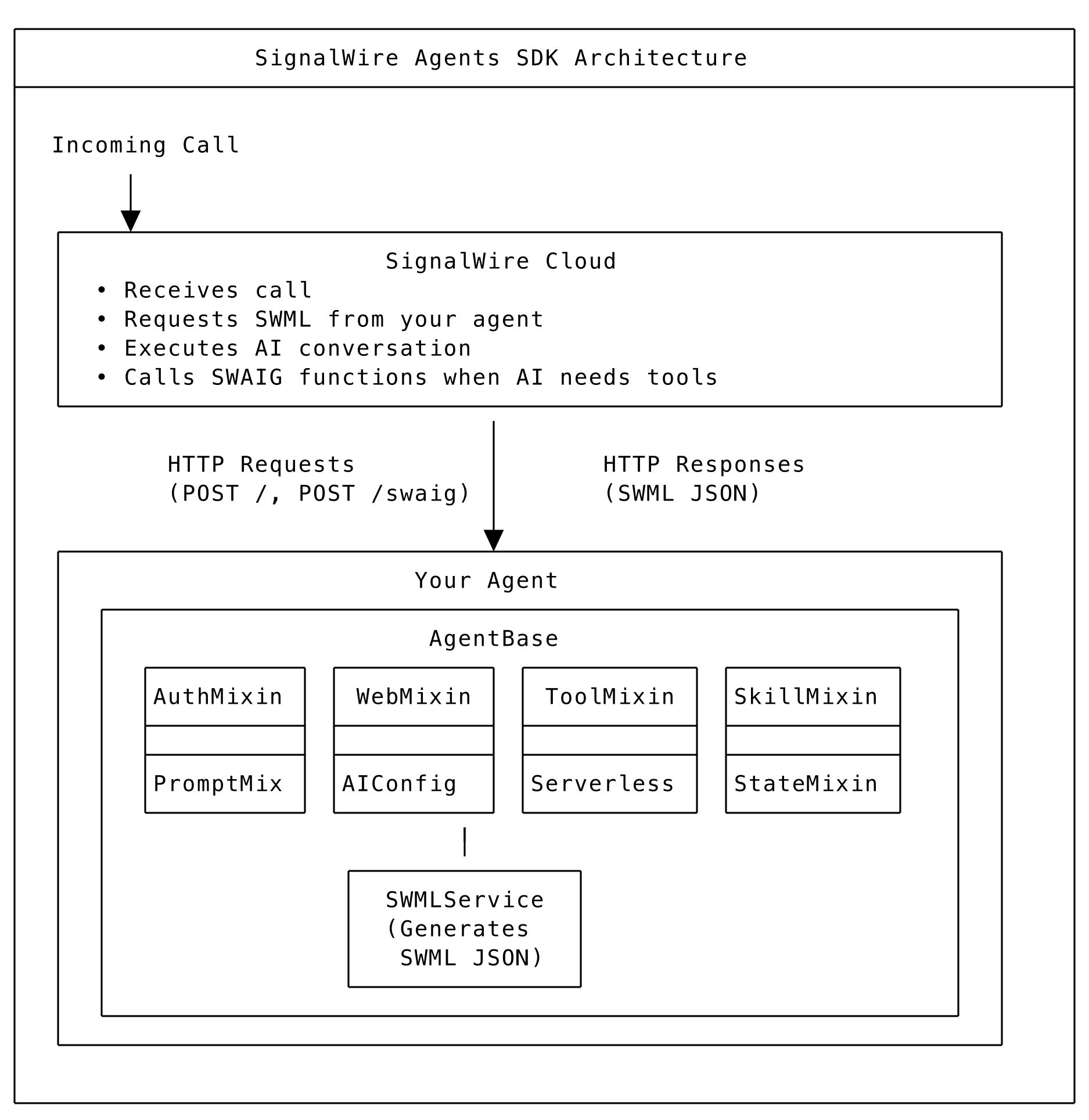
SignalWire Agents SDK Architecture
Key Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| AgentBase | The base class all agents inherit from |
| SWML | SignalWire Markup Language - JSON format for call instructions |
| SWAIG | SignalWire AI Gateway - System for AI to call your functions |
| Mixin | A class providing specific functionality to AgentBase |
| POM | Prompt Object Model - Structured prompt building |
| DataMap | Declarative REST API integration |
Chapter Contents
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Architecture | AgentBase class and mixin composition |
| SWML | Understanding SWML document structure |
| SWAIG | How AI calls your functions |
| Lifecycle | Request/response flow |
| Security | Authentication and token security |
Why These Concepts Matter
Understanding these core concepts helps you:
- Debug effectively - Know where to look when things go wrong
- Build efficiently - Use the right tool for each task
- Scale confidently - Understand how the system handles load
- Extend properly - Add custom functionality the right way
The Mixin Composition Pattern
AgentBase doesn't inherit from a single monolithic class. Instead, it combines eight specialized mixins:
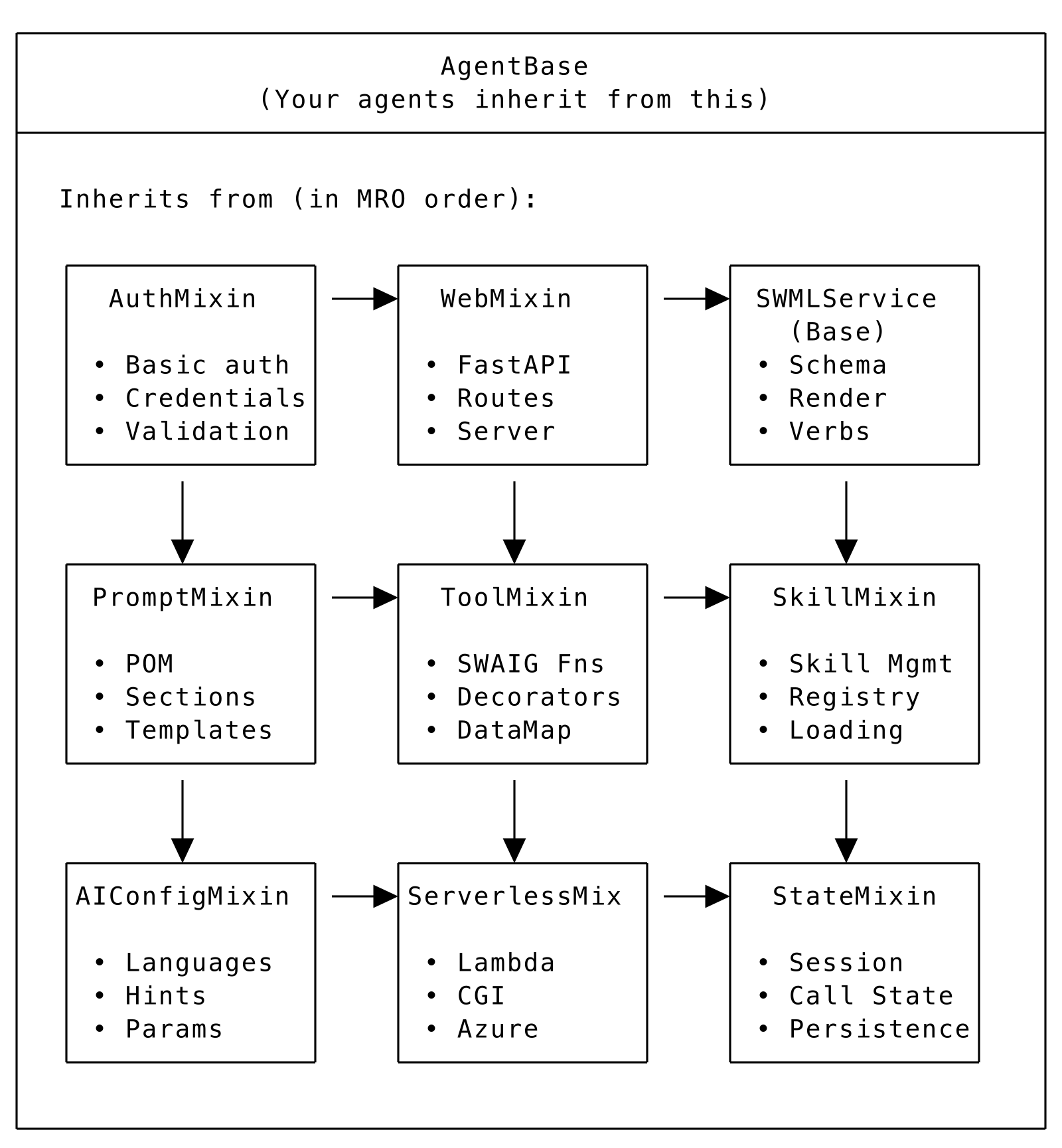
AgentBase Mixin Composition
Each Mixin's Role
AuthMixin - Authentication & Security
Handles basic HTTP authentication for webhook endpoints.
from signalwire_agents import AgentBase
class MyAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="my-agent")
# Auth credentials auto-generated or from environment:
# SWML_BASIC_AUTH_USER, SWML_BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD
Key methods:
- Validates incoming requests against stored credentials
- Generates credentials if not provided via environment
- Protects SWAIG function endpoints
WebMixin - HTTP Server & Routing
Manages the FastAPI application and HTTP endpoints.
# Automatically registers these routes:
# GET / → Returns SWML document
# POST / → Returns SWML document
# POST /swaig → Handles SWAIG function calls
# POST /post_prompt → Receives call summaries
# GET /debug → Debug information (dev only)
Key features:
- Runs uvicorn server via
agent.run() - Handles proxy detection (ngrok, load balancers)
- Manages request/response lifecycle
SWMLService - SWML Document Generation
The foundation for building SWML documents.
# SWMLService provides:
# - Schema validation against SWML spec
# - Verb handler registry
# - Document rendering pipeline
Key responsibilities:
- Validates SWML structure against JSON schema
- Registers verb handlers (answer, ai, connect, etc.)
- Renders final SWML JSON
PromptMixin - Prompt Management
Manages AI system prompts using POM (Prompt Object Model).
agent.prompt_add_section(
"Role",
"You are a helpful customer service agent."
)
agent.prompt_add_section(
"Guidelines",
body="Follow these rules:",
bullets=[
"Be concise",
"Be professional",
"Escalate when needed"
]
)
Key features:
- Structured prompt building with sections
- Support for bullets, subsections
- Post-prompt for call summaries
ToolMixin - SWAIG Function Management
Handles registration and execution of SWAIG functions.
agent.define_tool(
name="get_balance",
description="Get account balance",
parameters={
"account_id": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The account ID"
}
},
handler=self.get_balance
)
Key features:
- Multiple registration methods (define_tool, decorators, DataMap)
- Parameter validation
- Security token generation
SkillMixin - Skill Plugin Management
Loads and manages reusable skill plugins.
# Load built-in skill
agent.add_skill("datetime")
# Load skill with configuration
agent.add_skill("web_search",
google_api_key="...",
google_cx_id="..."
)
Key features:
- Auto-discovery of skill modules
- Dependency checking
- Configuration validation
AIConfigMixin - AI Behavior Configuration
Configures the AI's voice, language, and behavior parameters.
agent.add_language("English", "en-US", "rime.spore")
agent.set_params({
"end_of_speech_timeout": 500,
"attention_timeout": 15000
})
agent.add_hints(["SignalWire", "SWML", "AI agent"])
Key features:
- Voice and language settings
- Speech recognition hints
- AI behavior parameters
ServerlessMixin - Deployment Adapters
Provides handlers for serverless deployments.
# AWS Lambda
handler = agent.serverless_handler
# Google Cloud Functions
def my_function(request):
return agent.cloud_function_handler(request)
# Azure Functions
def main(req):
return agent.azure_function_handler(req)
Key features:
- Environment auto-detection
- Request/response adaptation
- URL generation for each platform
StateMixin - State Management
Manages session and call state.
# State is passed via global_data in SWML
# and preserved across function calls
Key features:
- Session tracking
- State persistence patterns
- Call context management
Key Internal Components
Beyond the mixins, AgentBase uses several internal managers:
ToolRegistry
- Stores SWAIG functions
- Handles function lookup
- Generates webhook URLs
PromptManager
- Manages prompt sections
- Builds POM structure
- Handles post-prompts
SessionManager
- Token generation
- Token validation
- Security enforcement
SkillManager
- Skill discovery
- Skill loading
- Configuration validation
SchemaUtils
- SWML schema loading
- Document validation
- Schema-driven help
VerbHandlerRegistry
- Verb registration
- Handler dispatch
- Custom verb support
Creating Your Own Agent
When you create an agent, you get all mixin functionality automatically:
from signalwire_agents import AgentBase, SwaigFunctionResult
class CustomerServiceAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="customer-service")
# AIConfigMixin methods
self.add_language("English", "en-US", "rime.spore")
self.set_params({"end_of_speech_timeout": 500})
# PromptMixin methods
self.prompt_add_section("Role", "You are a helpful agent.")
# ToolMixin methods
self.define_tool(
name="lookup_order",
description="Look up an order by ID",
parameters={
"order_id": {"type": "string", "description": "Order ID"}
},
handler=self.lookup_order
)
# SkillMixin methods
self.add_skill("datetime")
def lookup_order(self, args, raw_data):
order_id = args.get("order_id")
# Your business logic here
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Order {order_id}: Shipped, arrives tomorrow")
if __name__ == "__main__":
agent = CustomerServiceAgent()
agent.run() # WebMixin method
Benefits of This Architecture
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Separation of Concerns | Each mixin handles one domain |
| Easy to Understand | Look at one mixin for one feature |
| Extensible | Override specific mixin methods |
| Testable | Test mixins independently |
| Type-Safe | Full type hints throughout |
Next Steps
Now that you understand how AgentBase is structured, let's look at the SWML documents it generates.